
Chinese flag on dark blue background
Big Country | Electronics+ | Getty Images
The Asian Development Bank said that despite the economic slowdown, China will remain the largest growth engine of the world economy.
“Obviously, China will still play an important role in the coming period. They still account for nearly half of the GDP of the Asia-Pacific region,” Albert Parker, chief economist of the Asian Development Bank, said at a press conference on the bank’s Asian Development Outlook report.
“While growth is slowing, and we expect growth to continue to slow over the next few years… it is probably the largest contributor to global growth of any economy in the world,” Parker said.
The Asian Bank predicts that China’s GDP will grow at an annual rate of 4.8% in 2024, which is lower than the government’s target of “about 5%”. China’s economy will grow by 5.2% in 2023, reaching the official target of around 5%.
ADB data estimates that even if growth slows down, China will still account for 46% of the growth of developing Asian countries in 2024-2025.
China currently accounts for 18% and 48% respectively Global and Asia’s Gross Domestic ProductBased on purchasing power parity exchange rates, respectively, this is the measure used by the Asian Development Bank, World Bank and International Monetary Fund.
What about India?
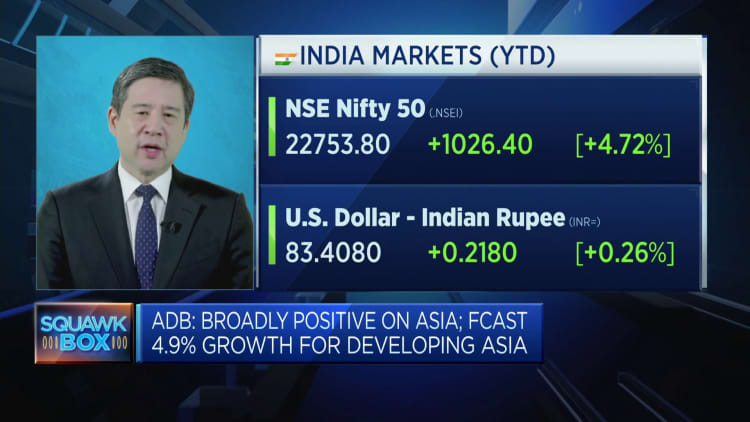
Indian The favorable economic trajectory has many touting the country’s role as a technology and manufacturing powerhouse and an attractive alternative to China. The South Asian country’s economy recently expanded at its fastest pace in six quarters, Growth of 8.4% exceeded expectations In the October-December quarter of the current financial year 2023-24.
“India’s importance to the region’s growth is increasing,” Parker told CNBC via email. The Asian Bank predicts that the country’s economic growth rate will be the highest in the region, reaching 7% in 2024 and 7.2% in 2025.
Parker said that while India’s economy was undoubtedly a “bright spot,” it was still smaller than China’s. On the purchasing power parity exchange rate metric, economists point out that China’s economy is still about two and a half times larger than India’s.
“So, on this benchmark, I think it will take a long time for India to really drive global growth,” he added.
In addition, the growth of developed economies is expected to slow down this year. The Asian Bank predicts that the GDP growth rate of the United States in 2023 will drop to 1.9% from 2.5% last year, and that of Japan will grow by 0.6% from 1.9% in 2023.
The bank also said in the report that it expects growth in developing Asia this year to be slightly stronger than forecast in December, as healthy domestic demand offsets the impact of China’s economic slowdown.
Despite rising energy prices, inflation in the Asia-Pacific region is also expected to fall from 3.3% in 2023 to 3.2% this year.





